Meanwhile, from their respective origins, each of its protocols has a previous meeting to the COP called meeting of the Parties (COP-MOP).
Mexico will host the 13th meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP 13), the eighth COP-MOP of the Cartagena Protocol (COP-MOP 8) and the second COP-MOP Nagoya Protocol (COP-MOP 2) The activities will be held from 2 to 17 December 2016 in Cancun, Quintana Roo.
During COP 13, about ten thousand participants, including representatives of the countries parties, observer countries, international organizations and others interested will meet in Cancun to negotiate agreements and commitments that give impulse to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity as well as the implementation of the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020 and the Aichi goals.
The administration of Mexico’s president, Enrique Peña Nieto, is committed to providing a propitious space and facilitate the development of the work of the countries party to support the fulfillment of the objectives of the CBD, the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011- 2020 and the Aichi goals.
In the context of the COP 13 will be also held various difusion events, exhibitions, presentations, fairs, forums (business, civil society, youth, indigenous people and local communities, cities and subnational governments, among others).
Objectives of Mexico at COP 13
In the context of the COP 13 Mexico will promote actions to support the implementation of the Strategic Plan 2011-2020 and its Aichi goals, so that it has been proposed as central theme: the integration of the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity in the plans, programs and sectoral and intersectoral policies with emphasis on agriculture, forestry, fisheries and tourism sectors.
This topic is expected to be written into the ministerial declaration to be adopted at the High Level Segment and in one of the decisions of the COP 13.
In addition, Mexico will use this space to promote the development of sectoral and intersectoral agendas in support to the implementation of the CBD and to show examples of success stories in integrating biodiversity in Mexico and other countries, seeking that they can be replicated.
|
Enhancing the effectiveness of Payments for Ecosystem Services (PES)
Biodiversity and ecosystems provide many critical life support functions and benefits for human wellbeing, security and economic growth, including food, clean water, recreational services and climate regulation. Despite its significant values, biodiversity worldwide is being lost, in some areas at a rapid rate.
Given these losses, there is an urgent need for firstly, greater application of policies and incentives to promote the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity and ecosystem services, and secondly, a more efficient use of available finance in existing biodiversity programmes. PES is a flexible, incentive-based mechanism that has potential to deliver in both of these areas. This Thematic Issue of Science for Environment Policy explores research which can help guide effective PES schemes. Under PES agreements, a user or beneficiary of an ecosystem service provides payments to individuals or communities whose management decisions and practices influence the provision of ecosystem services.
Read more...
About BISE
 The Biodiversity Information System for Europe (BISE) is a single entry point for data and information on biodiversity in the EU. Bringing together facts and figures on biodiversity and ecosystem services, it links to related policies, environmental data centres, assessments and research findings from various sources. It is being developed to strengthen the knowledge base and support decision-making on biodiversity. The Biodiversity Information System for Europe (BISE) is a single entry point for data and information on biodiversity in the EU. Bringing together facts and figures on biodiversity and ecosystem services, it links to related policies, environmental data centres, assessments and research findings from various sources. It is being developed to strengthen the knowledge base and support decision-making on biodiversity.
BISE as a partnership
BISE is a partnership between the European Commission (DG Environment, Joint Research Centre and Eurostat) and the European Environment Agency. It incorporates the network of the European Clearing House Mechanism within the context of the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Read more...
From the Rio Conventions’ Ecosystems Pavilion: It is now widely recognized that climate change, land degradation and biodiversity are interconnected, not only through effects of climate change on biodiversity and land management, but also through changes in biodiversity and ecosystem functioning that affect climate change. The carbon cycle and the water cycle, arguably the two most important large-scale processes for life on Earth, both depend on biodiversity – at genetic, species, and ecosystem levels and can yield feedbacks to climate change.
 Maintaining and restoring healthy ecosystems plays a key role in adapting to and mitigating climate change through biodiversity conservation, sustainable use and sustainable land management and yields multiple environmental, economic and social benefits. Maintaining and restoring healthy ecosystems plays a key role in adapting to and mitigating climate change through biodiversity conservation, sustainable use and sustainable land management and yields multiple environmental, economic and social benefits.
Ecosystem-based approaches provide an important route to sustainable action and represent a vital insurance policy against irreversible damage from climate change, whereas failure to acknowledge the relationship between climate change and biodiversity and failure to act swiftly and in an integrated manner could undermine efforts for improvements in both areas.
However, enormous pressures have been put on ecosystems to support the ever-growing demand for natural resources over recent years. Ecosystem services that are central to adaptation include goods, such as food, fodder and pharmaceutical products, and services, such as nutrient cycling and hydrological flows.
This was discussed on Monday, 18 October, 2010 ion Nagoya, Japan, during the tenth meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity.
Read more...
By J.E. Nigros
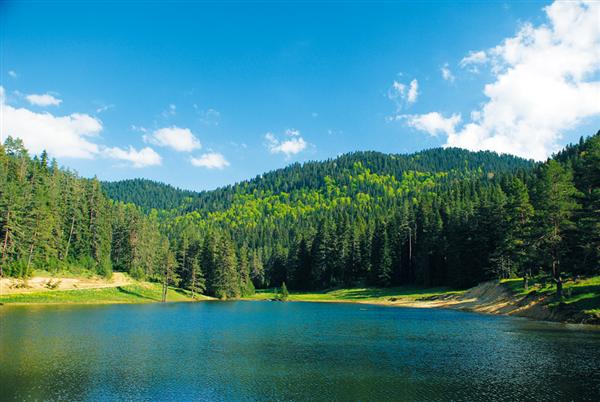

The people of Turkey have long been aware of the unique biodiversity of their country and the importance of preserving natural habitats. More than a millennium ago, the folk poet Dede Korkut wrote this prayer:
May our big shade tree never be cut down
May our forests never thin out
May our clear running streams never dry up
May we never be deprived of hope
May our wings never be broken
May our household fire keep burning
While Dede Korkut’s prayer seems to consign the fate of the environment to Allah and to chance, modern Turkish people know they must pass laws and enforce environmental policies to protect their environment.
Since the 1950’s, Turkey has been developing its environmental policies. Since 1997, the rules of the Convention of Biological Diversity have been in force. Turkey is a party to all relevant international conventions having to do with the conservation of biodiversity. According to the ever-evolving document, the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan, Turkish legislation, however, has never been “harmonized from a consistent environmental point of view which presents frequent problems of overlap and lack of legal mandates for institutions.”
Read more...
The UN has launched the International Year of Biodiversity, warning that the ongoing loss of species around the world is affecting human well-being.
Eight years ago, governments pledged to reduce the rate of biodiversity loss by 2010, but the pledge will not be met. The expansion of human cities, farming and infrastructure is the main reason. Speaking at the launch in Berlin, German premier Angela Merkel urged the establishment of a new panel to collate scientific findings on the issue.
Achim Steiner, executive director of the UN Environment Programme (UNEP), urged governments and their leaders to renew their commitment to curbing biodiversity loss even though the 2010 goal will be missed. "The urgency of the situation demands that as a global community we not only reverse the rate of loss, but that we stop the loss altogether and begin restoring the ecological infrastructure that has been damaged and degraded over the previous century or so," he said.
Read more...
 Upcoming Ethnobiology Course in Turkey Upcoming Ethnobiology Course in Turkey
Kars, Turkey: As part of our international program, GDF is co-organizing an ethnobiological research methods short course with a particular focus on applied research in Turkey, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. The course, to be held 13 - 21 September 2010 in Kars, will explore how global trends are impacting local communities and how researchers can interact with these communities in transition, helping them to draw upon their biocultural diversity to adapt to a changing world. Gary Martin will be conducting the course in collaboration with Dr. Füsun Ertuğ and Dr. Çagan Şekercioğlu (KuzeyDoga Society and Stanford University). Interested students can find further details on how to apply at the Biocultural Diversity Learning Network.
http://www.global-diversity.org/upcoming-ethnobiology-course-turkey
 Definitions Definitions
Biological diversity, or ‘biodiversity’, simply means the variety of life on Earth. Stated another way, it refers to the variability among living organisms from all sources including, inter alia, terrestrial, marine and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are part; this includes diversity within species, between species and of ecosystems.
Ecology is the study of the relationships and interactions between living organisms and their natural or developed environment.
Ecosystem services are the benefits of nature to people - households, communities and economies. They comprise provisioning, regulating, supporting and cultural services.
Ecological Footprint of an individual, a city, a country, or humanity is a measure of how much productive land and water they require to produce all the resources they consume and to absorb all the waste they generate, using prevailing technology. The term was coined by William E. Rees and Mathis Wackernagel in the early 1990s. The Ecological Footprint is measured in global hectares. Today, humanity's Ecological Footprint is over 23% larger than the planet can regenerate. (http://www.footprintnetwork.org/) In other words, it now takes more than one year and two months for the Earth to regenerate what we use in a single year. We maintain this overshoot by liquidating the planet's ecological resources.
Read more...
 UNESCO UNESCO, in collaboration with the Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and Centre Sciences, Orléans - a French resource centre specialized in the production of travelling scientific exhibitions - have joined efforts to create a travelling exhibition to convey the key IYB messages on biodiversity. The exhibition aims to enhance public awareness of the importance of conserving biodiversity, of the threats to biodiversity and demonstrates how the global community is working to ensure its conservation and sustainable use now and in the future. In particular, the exhibition explores the multiple aspects of biodiversity contributing to human well-being and describes the direct and indirect factors contributing to biodiversity loss. There is special emphasis on the economic aspects of biodiversity and the links between cultural and biological diversity. The exhibit is intended for multiple audiences, including policy- and decision-makers, conservation practitioners, museums and educational institutions. The use of simple language and attractive visual elements contribute to making the exhibition equally accessible to a wider public.
The exhibition, in English and French, organized around 7 themes comprises in total 42 panels with 6 panels per theme. The physical copy of the exhibition will be enhanced throughout the IYB with interactive elements. Exhibitors are invited to display local examples of biodiversity alongside the panels.
Related links
Date: 2-4 November 2010
Venue: Royal Marine Hotel, Dun Laoghaire, Republic of Ireland
BACKGROUND
In the International Year of Biodiversity what do we have to celebrate? What has been achieved? What targets have been met? What still needs to be done? What tools are available to improve biodiversity conservation in the future?
Heads of State and Government undertook in 2001 to halt the decline of biodiversity in the EU by 2010 and to restore habitats and natural systems. In 2002, they also joined some 130 world leaders in agreeing to significantly reduce the rate of biodiversity loss globally by 2010.
In May 2006, the European Commission adopted a communication on "Halting Biodiversity Loss by 2010 – and Beyond: Sustaining ecosystem services for human well-being". The Communication underlined the importance of biodiversity protection as a pre-requisite for sustainable development, as well as setting out a detailed EU Biodiversity Action Plan to achieve this.
Read more...
|
|



 Biodiversity
Biodiversity




 Upcoming Ethnobiology Course in Turkey
Upcoming Ethnobiology Course in Turkey Definitions
Definitions UNESCO, in collaboration with the Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and Centre Sciences, Orléans - a French resource centre specialized in the production of travelling scientific exhibitions - have joined efforts to create a travelling exhibition to convey the key IYB messages on biodiversity.
UNESCO, in collaboration with the Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and Centre Sciences, Orléans - a French resource centre specialized in the production of travelling scientific exhibitions - have joined efforts to create a travelling exhibition to convey the key IYB messages on biodiversity.