ENVIRONMENT
- Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive human intervention, including all vegetation, animals, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries.
- Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from human activity.
The natural environment is contrasted with the built environment, which comprises the areas and components that are strongly influenced by humans. A geographical area is regarded as a natural environment (with an indefinite article), if the human impact on it is kept under a certain limited level (similar to section 1 above).
Contents |
Composition
Geological activity
 The Earth's crust, or Continental crust, is the outermost solid land surface of the planet, is chemically and mechanically different from underlying mantles, and has been generated largely by igneous processes in which magma (molten rock) cools and solidifies to form solid land. Plate tectonics, mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes are geological phenomena that can be explained in terms of energy transformations in the Earth's crust[3], and might be thought of as the process by which the earth resurfaces itself. Beneath the Earth's crust lies the mantle which is heated by the radioactive decay of heavy elements. The mantle is not quite solid and consists of magma which is in a state of semi-perpetual convection. This convection process causes the lithospheric plates to move, albeit slowly. The resulting process is known as plate tectonics.[4][5][6][7] Volcanoes result primarily from the melting of subducted crust material. Crust material that is forced into the Asthenosphere melts, and some portion of the melted material becomes light enough to rise to the surface, giving birth to volcanoes![5]
The Earth's crust, or Continental crust, is the outermost solid land surface of the planet, is chemically and mechanically different from underlying mantles, and has been generated largely by igneous processes in which magma (molten rock) cools and solidifies to form solid land. Plate tectonics, mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes are geological phenomena that can be explained in terms of energy transformations in the Earth's crust[3], and might be thought of as the process by which the earth resurfaces itself. Beneath the Earth's crust lies the mantle which is heated by the radioactive decay of heavy elements. The mantle is not quite solid and consists of magma which is in a state of semi-perpetual convection. This convection process causes the lithospheric plates to move, albeit slowly. The resulting process is known as plate tectonics.[4][5][6][7] Volcanoes result primarily from the melting of subducted crust material. Crust material that is forced into the Asthenosphere melts, and some portion of the melted material becomes light enough to rise to the surface, giving birth to volcanoes![5]Oceanic activity
 An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface (an area of some 361 million square kilometers) is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas. More than half of this area is over 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) deep. Average oceanic salinity is around 35 parts per thousand (ppt) (3.5%), and nearly all seawater has a salinity in the range of 30 to 38 ppt. Though generally recognized as several 'separate' oceans, these waters comprise one global, interconnected body of salt water often referred to as the World Ocean or global ocean.[8][9] This concept of a global ocean as a continuous body of water with relatively free interchange among its parts is of fundamental importance to oceanography.[10]
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface (an area of some 361 million square kilometers) is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas. More than half of this area is over 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) deep. Average oceanic salinity is around 35 parts per thousand (ppt) (3.5%), and nearly all seawater has a salinity in the range of 30 to 38 ppt. Though generally recognized as several 'separate' oceans, these waters comprise one global, interconnected body of salt water often referred to as the World Ocean or global ocean.[8][9] This concept of a global ocean as a continuous body of water with relatively free interchange among its parts is of fundamental importance to oceanography.[10]
The major oceanic divisions are defined in part by the continents, various archipelagos, and other criteria: these divisions are (in descending order of size) the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean (which is sometimes subsumed as the southern portions of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans), and the Arctic Ocean (which is sometimes considered a sea of the Atlantic). The Pacific and Atlantic may be further subdivided by the equator into northerly and southerly portions. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays and other names. There are also salt lakes, which are smaller bodies of landlocked saltwater that are not interconnected with the World Ocean. Two notable examples of salt lakes are the Aral Sea and the Great Salt Lake.
Rivers and lakes
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing toward an ocean, a lake, a sea or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including stream, creek, brook, rivulet, and rill; there is no general rule that defines what can be called a river. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; one example is Burn in Scotland and North-east England. Sometimes a river is said to be larger than a creek,[11] but this is not always the case, due to vagueness in the language.[12] A river is part of the hydrological cycle. Water within a river is generally collected from precipitation through surface runoff, groundwater recharge, springs, and the release of stored water in natural ice and snowpacks (i.e., from glaciers).
A lake (from Latin lacus) is a terrain feature (or physical feature), a body of liquid on the surface of a world that is localized to the bottom of basin (another type of landform or terrain feature; that is, it is not global) and moves slowly if it moves at all. On Earth, a body of water is considered a lake when it is inland, not part of the ocean, is larger and deeper than a pond, and is fed by a river.[13][14] The only world other than Earth known to harbor lakes is Titan, Saturn's largest moon, which has lakes of ethane, most likely mixed with methane. It is not known if Titan's lakes are fed by rivers, though Titan's surface is carved by numerous river beds. Natural lakes on Earth are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing or recent glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers. In some parts of the world, there are many lakes because of chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last Ice Age. All lakes are temporary over geologic time scales, as they will slowly fill in with sediments or spill out of the basin containing them.
Atmosphere, climate and weather
The atmosphere of the Earth serves as a key factor in sustaining the planetary ecosystem. The thin layer of gases that envelops the Earth is held in place by the planet's gravity. Dry air consists of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% argon and other inert gases, carbon dioxide, etc.; but air also contains a variable amount of water vapor. The atmospheric pressure declines steadily with altitude, and has a scale height of about 8 kilometres at the Earth's surface: the height at which the atmospheric pressure has declined by a factor of e (a mathematical constant equal to 2.71...).[15][16] The ozone layer of the Earth's atmosphere plays an important role in depleting the amount of ultraviolet (UV) radiation that reaches the surface. As DNA is readily damaged by UV light, this serves to protect life at the surface. The atmosphere also retains heat during the night, thereby reducing the daily temperature extremes.
Effects of global warming
The potential dangers of global warming are being increasingly studied by a wide global consortium of scientists, who are increasingly concerned about the potential long-term effects of global warming on our natural environment and on the planet. Of particular concern is how climate change and global warming caused by anthropogenic, or human-made releases of greenhouse gases, most notably carbon dioxide, can act interactively, and have adverse effects upon the planet, its natural environment and humans' existence. Efforts have been increasingly focused on the mitigation of greenhouse gases that are causing climatic changes, on developing adaptative strategies to global warming, to assist humans, animal and plant species, ecosystems, regions and nations in adjusting to the effects of global warming. Some examples of recent collaboration to address climate change and global warming include:
- The United Nations Framework Convention Treaty and convention on Climate Change, to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system.[17]
- The Kyoto Protocol, which is the protocol to the international Framework Convention on Climate Change treaty, again with the objective of reducing greenhouse gases in an effort to prevent anthropogenic climate change.[18]
- The Western Climate Initiative, to identify, evaluate, and implement collective and cooperative ways to reduce greenhouse gases in the region, focusing on a market-based cap-and-trade system.[19]
A significantly profound challenge is to identify the natural environmental dynamics in contrast to environmental changes not within natural variances. A common solution is to adapt a static view neglecting natural variances to exist. Methodologically, this view could be defended when looking at processes which change slowly and short time series, while the problem arrives when fast processes turns essential in the object of the study.
Life
Although there is no universal agreement on the definition of life, scientists generally accept that the biological manifestation of life is characterized by organization, metabolism, growth, adaptation, response to stimuli and reproduction.[20] Life may also be said to be simply the characteristic state of organisms.
Properties common to terrestrial organisms (plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea and bacteria) are that they are cellular, carbon-and-water-based with complex organization, having a metabolism, a capacity to grow, respond to stimuli, and reproduce. An entity with these properties is generally considered life. However, not every definition of life considers all of these properties to be essential. Human-made analogs of life may also be considered to be life.
The biosphere is the part of Earth's outer shell — including air, land, surface rocks and water — within which life occurs, and which biotic processes in turn alter or transform. From the broadest geophysiological point of view, the biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interaction with the elements of the lithosphere (rocks), hydrosphere (water), and atmosphere (air). Currently the entire Earth contains over 75 billion tons (150 trillion pounds or about 6.8 x 1013 kilograms) of biomass (life), which lives within various environments within the biosphere.[21]
Ecosystems
An ecosystem is a natural unit consisting of all plants, animals and micro-organisms (biotic factors) in an area functioning together with all of the non-living physical (abiotic) factors of the environment.[24]
Central to the ecosystem concept is the idea that living organisms are continually engaged in a highly interrelated set of relationships with every other element constituting the environment in which they exist. Eugene Odum, one of the founders of the science of ecology, stated: "Any unit that includes all of the organisms (ie: the "community") in a given area interacting with the physical environment so that a flow of energy leads to clearly defined trophic structure, biotic diversity, and material cycles (ie: exchange of materials between living and nonliving parts) within the system is an ecosystem."[25] The human ecosystem concept is then grounded in the deconstruction of the human/nature dichotomy, and the emergent premise that all species are ecologically integrated with each other, as well as with the abiotic constituents of their biotope.
A greater degree of species or biological diversity - popularly referred to as Biodiversity - of an ecosystem may contribute to greater resilience of an ecosystem, because there are more species present at a location to respond to change and thus "absorb" or reduce its effects. This reduces the effect before the ecosystem's structure is fundamentally changed to a different state. This is not universally the case and there is no proven relationship between the species diversity of an ecosystem and its ability to provide goods and services on a sustainable level: Humid tropical forests produce very few goods and direct services and are extremely vulnerable to change, while many temperate forests readily grow back to their previous state of development within a lifetime after felling or a forest fire. Some grasslands have been sustainably exploited for thousands of years (Mongolia, Africa, European peat and mooreland communities).
The term ecosystem can also pertain to human-made environments, such as human ecosystems and human-influenced ecosystems, and can describe any situation where there is relationship between living organisms and their environment. Fewer areas on the surface of the earth today exist free from human contact, although some genuine wilderness areas continue to exist without any forms of human intervention.
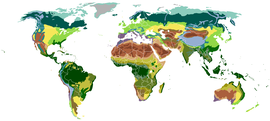
Biomes
Biomes are terminologically similar to the concept of ecosystems, and are climatically and geographically defined areas of ecologically similar climatic conditions such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, often referred to as ecosystems. Biomes are defined based on factors such as plant structures (such as trees, shrubs, and grasses), leaf types (such as broadleaf and needleleaf), plant spacing (forest, woodland, savanna), and climate. Unlike ecozones, biomes are not defined by genetic, taxonomic, or historical similarities. Biomes are often identified with particular patterns of ecological succession and climax vegetation.
Wilderness
Wilderness is generally defined as a natural environment on Earth that has not been significantly modified by human activity. The WILD Foundation goes into more detail, defining wilderness as: "The most intact, undisturbed wild natural areas left on our planet - those last truly wild places that humans do not control and have not developed with roads, pipelines or other industrial infrastructure."[26] Wilderness areas and protected parks are considered important for the survival of certain species, ecological studies, conservation, solitude, and recreation. Wilderness is deeply valued for cultural, spiritual, moral, and aesthetic reasons. Some nature writers believe wilderness areas are vital for the human spirit and creativity. [27]
The word, "wilderness", derives from the notion of wildness; in other words that which is not controllable by humans. The word's etymology is from the Old English wildeornes, which in turn derives from wildeor meaning wild beast (wild + deor = beast, deer).[28] From this point of view, it is the wildness of a place that makes it a wilderness. The mere presence or activity of people does not disqualify an area from being "wilderness." Many ecosystems that are, or have been, inhabited or influenced by activities of people may still be considered "wild." This way of looking at wilderness includes areas within which natural processes operate without very noticeable human interference.
Biogeochemical Cycles
|
Nitrogen Cycle 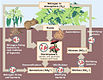 |
Water Cycle 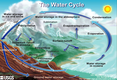 |
|
Carbon Cycle 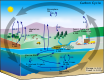 |
Oxygen Cycle 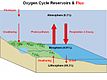 |
Global biogeochemical cycles are critical to life, most notably those of water, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus.[29]
- The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle that describes the transformations of nitrogen and nitrogen-containing compounds in nature. It is a cycle which includes gaseous components.
- The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. Since the water cycle is truly a "cycle," there is no beginning or end. Water can change states among liquid, vapor, and ice at various places in the water cycle. Although the balance of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time, individual water molecules can come and go.
- The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth.
- The oxygen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle that describes the movement of oxygen within and between its three main reservoirs: the atmosphere (air), the biosphere (living things), and the lithosphere (Earth's crust). The main driving factor of the oxygen cycle is photosynthesis, which is responsible for the modern Earth's atmosphere and life.
Challenges
It is the common understanding of natural environment that underlies environmentalism — a broad political, social, and philosophical movement that advocates various actions and policies in the interest of protecting what nature remains in the natural environment, or restoring or expanding the role of nature in this environment. While true wilderness is increasingly rare, wild nature (e.g., unmanaged forests, uncultivated grasslands, wildlife, wildflowers) can be found in many locations previously inhabited by humans.
Goals commonly expressed by environmental scientists include:
- Reduction and clean up of pollution, with future goals of zero pollution;
- Cleanly converting non-recyclable materials into energy through direct combustion or after conversion into secondary fuels;
- Reducing societal consumption of non-renewable fuels;
- Development of alternative, green, low-carbon or renewable energy sources;
- Conservation and sustainable use of scarce resources such as water, land, and air;
- Protection of representative or unique or pristine ecosystems;
- Preservation of threatened and endangered species extinction;
- The establishment of nature and biosphere reserves under various types of protection; and, most generally, the protection of biodiversity and ecosystems upon which all human and other life on earth depends.
Very large development projects - megaprojects - pose special challenges and risks to the natural environment. Major dams and power plants are cases in point. The challenge to the environment from such projects is growing because more and bigger megaprojects are being built, in developed and developing nations alike.[30]
References
- ^ Earth's Spheres. ©1997-2000. Wheeling Jesuit University/NASA Classroom of the Future. Retrieved November 11, 2007.
- ^ Wordnet Search: Earth science
- ^ Earth's Energy Budget
- ^ Simison par. 7
- ^ a b Adams 94,95,100,102
- ^ Smith 13-17,218,G-6
- ^ Oldroyd 101,103,104
- ^ "Ocean". The Columbia Encyclopedia. 2002. New York: Columbia University Press
- ^ "Distribution of land and water on the planet". UN Atlas of the Oceans
- ^ Spilhaus, Athelstan F. 1942 (Jul.). "Maps of the whole world ocean." Geographical Review (American Geographical Society). Vol. 32 (3): pp. 431-5.
- ^ River, Wordnet
- ^ USGS - U.S. Geological Survey - faqs, #17 What is the difference between mountain, hill, and peak; lake and pond; or river and creek?
- ^ Brittanica online. "Lake (physical feature)". http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/328083/lake. Retrieved 2008-06-25. "[a Lake is] any relatively large body of slowly moving or standing water that occupies an inland basin of appreciable size. Definitions that precisely distinguish lakes, ponds, swamps, and even rivers and other bodies of nonoceanic water are not well established. It may be said, however, that rivers and streams are relatively fast moving; marshes and swamps contain relatively large quantities of grasses, trees, or shrubs; and ponds are relatively small in comparison to lakes. Geologically defined, lakes are temporary bodies of water."
- ^ "[http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/lake a body of fresh or salt water of considerable size, surrounded by land. Dictionary.com definition]". http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/lake a body of fresh or salt water of considerable size, surrounded by land.. Retrieved 2008-06-25.
- ^ "Ideal Gases under Constant Volume, Constant Pressure, Constant Temperature, & Adiabatic Conditions". NASA. http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/K-12/Numbers/Math/Mathematical_Thinking/ideal_gases_under_constant.htm. Retrieved 2007-01-07.
- ^ Pelletier, Jon D. (2002). "Natural variability of atmospheric temperatures and geomagnetic intensity over a wide range of time scales". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 99: 2546–2553. doi:10.1073/pnas.022582599. PMID 11875208.
- ^ United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change Retrieved August 2008.
- ^ Kyoto Protocol from United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, Retrieved August 2008.
- ^ Western Climate Initiative, Retrieved on Feb 12, 2009.
- ^ "Definition of Life". California Academy of Sciences. 2006. http://www.calacademy.org/exhibits/xtremelife/what_is_life.php. Retrieved 2007-01-07.
- ^ The figure "about one-half of one percent" takes into account the following (See, e.g., Leckie, Stephen (1999). "How Meat-centred Eating Patterns Affect Food Security and the Environment". For hunger-proof cities : sustainable urban food systems. Ottawa: International Development Research Centre. ISBN 0-88936-882-1., which takes global average weight as 60 kg.), the total human biomass is the average weight multiplied by the current human population of approximately 6.5 billion (see, e.g., "World Population Information". U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/ipc/www/world.html. Retrieved September 28 2006.): Assuming 60–70 kg to be the average human mass (approximately 130–150 lb on the average), an approximation of total global human mass of between 390 billion (390×109) and 455 billion kg (between 845 billion and 975 billion lb, or about 423 million-488 million short tons). The total biomass of all kinds on earth is estimated to be in excess of 6.8 x 1013 kg (75 billion short tons). By these calculations, the portion of total biomass accounted for by humans would be very roughly 0.6%.
- ^ http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Newsroom/view.php?id=28907
- ^ http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2005/12/051205163236.htm
- ^ Robert W. Christopherson (1996). Geosystems: An Introduction to Physical Geography. Prentice Hall Inc.
- ^ Odum EP (1971) Fundamentals of ecology, third edition, Saunders New York
- ^ The WILD Foundation
- ^ No Man's Garden by Daniel B. Botkin p155-157
- ^ "Wilderness", in The Collins English Dictionary (2000)
- ^ Smil, V. (2000). Cycles of Life. New York: Scientific American Library. ISBN 9780716750796.
- ^ *Flyvbjerg, Bent, Nils Bruzelius, and Werner Rothengatter, 2003. Megaprojects and Risk: An Anatomy of Ambition (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
Further reading
- Adams, Simon; David Lambert (2006). Earth Science: An illustrated guide to science. New York NY 10001: Chelsea House. pp. 20. ISBN 0-8160-6164-5.
- "Earth's Energy Budget". Oklahoma Climatological Survey. 1996-2004. http://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/EnergyBudget.html. Retrieved 2007-11-17.
- Oldroyd, David (2006). Earth Cycles: A historical perspective. Westport, Connicticut: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-33229-0.
- Simison, W. Brian (2007-02-05). "The mechanism behind plate tectonics". http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/geology/tecmech.html. Retrieved 2007-11-17.
- Smith, Gary A.; Aurora Pun (2006). How Does the Earth Work?. Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458: Pearson Prentice Hall. pp. 5. ISBN 0-13-034129-0.
Source: Wikipedia