 National and international wind energy industries and wind power technologies shall meet under a specialized exhibition, WindTech Istanbul, between the dates of 13-16 October 2010 in Istanbul for the first time in Turkey. WindTech is an exhibition, which targets the wind energy sector and which meets this sector under single roof. National and international wind energy industries and wind power technologies shall meet under a specialized exhibition, WindTech Istanbul, between the dates of 13-16 October 2010 in Istanbul for the first time in Turkey. WindTech is an exhibition, which targets the wind energy sector and which meets this sector under single roof.
WindTech Istanbul Wind Energy Trade Fair will take place in Istanbul Lutfi Kirdar Convention and Exhibition Centre (ICEC).
Objectives of WindTech Istanbul:
- To prepare a foundation for the creation of wind energy industry, to develop it and to provide contribution for it,
- Meeting of the Turkish investors with the equipment suppliers,
- To meet the foreigner investor with the Turkish producer in Turkey, where it is a great potential in the field of energy in terms of the investment and the production,
- To emphasize the fact that Turkey should search for its energy needs on the alternative sources and should direct itself towards renewable sources,
- To support the domestic industry and the production of turbines,
- To introduce the fields of use of wind energy,
- To create a platform for projects, which would increase the industrial efficiency,
- To show the importance of the need to go for variation for the energy supply and of the vitality of evaluation of our national energy sources and to underline that these are priority issues, (Minister of Energy and Natural Sources, Mr. Yildiz, has stated that, “we require to meet 30% of our total energy port folio from these sources, together with renewable energy sources and natural sources until 2030.This is a number, which is even above the EU average”)
- To play a triggering role for the start of the investment projects, which will be carried out in this filed, after the Draft Law with regards to make changes in the law, which is related to the Use of Renewable Energy Sources with regards to the Production of the Electrical Energy,
- To create a environment for the implementation of the investments, which will provide for the implementation of the investments that would be required and would be sufficient with regards to the security of the supply,
- To underline for the fact that the wind energy, which is the environment friendly, with minimum amount of carbon gas discharge, clean and widely available, form of energy due to the sanctions of the agreements like the Kyoto Protocol, etc, in order to have preventive measures for important issues like, global warming, change of the climate,
- To achieve the target, where it is thought that Turkey might have 20.000 megawatt of wind power by 2020.
|
Biodiesel Burns Significantly Cleaner than Diesel
 Biodiesel is renewable, nontoxic, and biodegradable. Compared to diesel, biodiesel burns significantly cleaner. It produces fewer air pollutants like particulates, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and air toxics. However, it does slightly increase emissions of nitrogen oxides. Biodiesel is renewable, nontoxic, and biodegradable. Compared to diesel, biodiesel burns significantly cleaner. It produces fewer air pollutants like particulates, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and air toxics. However, it does slightly increase emissions of nitrogen oxides.
A Fuel That Smells Like French Fries
Biodiesel produces less black smoke than regular diesel, and it smells better, too. Sometimes biodiesel exhaust smells like french fries!
A Fuel With No Sulfur
Regular diesel fuel contains sulfur. Sulfur can cause damage to the environment when it is burned in fuels. The amount of sulfur in diesel fuel is regulated by the Federal government.
When sulfur is removed from regular diesel fuel, the fuel doesn't work as well. Adding a small amount of biodiesel can fix the problem. Biodiesel has no sulfur, so it can reduce sulfur levels in the Nation's diesel fuel supply while making engines run smoother.
"Biofuels" are transportation fuels like ethanol and biodiesel that are made from biomass materials. These fuels are usually blended with the petroleum fuels — gasoline and diesel fuel, but they can also be used on their own. Using ethanol or biodiesel means we don't burn quite as much fossil fuel. Ethanol and biodiesel are usually more expensive than the fossil fuels that they replace, but they are also cleaner-burning fuels, producing fewer air pollutants.
 What Is Ethanol? What Is Ethanol?
Ethanol is an alcohol fuel made from the sugars found in grains, such as:
Other sources of sugars to produce ethanol include:
- Potato skins
- Rice
- Sugar cane
- Sugar beets
- Yard clippings
- Bark
- Switchgrass
Most of the ethanol used in the United States today is distilled from corn. Scientists are working on cheaper ways to make ethanol by using all parts of plants and trees rather than just the grain. Farmers are experimenting with "woody crops," mostly small poplar trees and switchgrass, to see if they can be grown cheaply and abundantly.
 Ethanol Is Blended With Gasoline Ethanol Is Blended With Gasoline
About 99% of the ethanol produced in the United States is used to make "E10" or "gasohol," a mixture of 10% ethanol and 90% gasoline. Any gasoline powered engine can use E10, but only specially made vehicles can run on E85, a fuel that is 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline.
What Is Biodiesel?
Biodiesel is a fuel made from vegetable oils, fats, or greases — such as recycled restaurant grease. Biodiesel fuel can be used in diesel engines without changing them. It is the fastest growing alternative fuel in the United States. Biodiesel, a renewable fuel, is safe, biodegradable, and produces lower levels of most air pollutants than petroleum-based products.
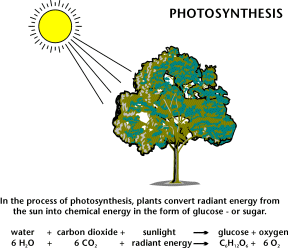 Renewable Energy from Plants and Animals Renewable Energy from Plants and Animals
Biomass is organic material made from plants and animals. Biomass contains stored energy from the sun. Plants absorb the sun's energy in a process called photosynthesis. The chemical energy in plants gets passed on to animals and people that eat them.
Biomass is a renewable energy source because we can always grow more trees and crops, and waste will always exist. Some examples of biomass fuels are wood, crops, manure, and some garbage.
When burned, the chemical energy in biomass is released as hyeat. If you have a fireplace, the wood you burn in it is a biomass fuel. Wood waste or garbage can be burned to produce steam for making electricity, or to provide heat to industries and homes.
Converting Biomass to Other Forms of Energy
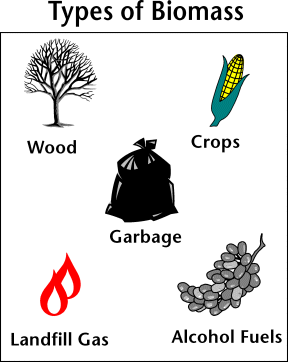 Burning biomass is not the only way to release its energy. Biomass can be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as methane gas or transportation fuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel. Burning biomass is not the only way to release its energy. Biomass can be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as methane gas or transportation fuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel.
Methane gas is the main ingredient of natural gas. Smelly stuff, like rotting garbage, and agricultural and human waste, release methane gas — also called "landfill gas" or "biogas."
Crops like corn and sugar cane can be fermented to produce ethanol. Biodiesel, another transportation fuel, can be produced from left-over food products like vegetable oils and animal fats.
How Much Biomass Is Used for Fuel?
Biomass fuels provide about 4% of the energy used in the United States. Researchers are trying to develop ways to burn more biomass and less fossil fuels. Using biomass for energy may cut back on waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy from the Sun
 The sun has produced energy for billions of years. Solar energy is the sun’s rays (solar radiation) that reach the Earth. This energy can be converted into other forms of energy, such as heat and electricity. The sun has produced energy for billions of years. Solar energy is the sun’s rays (solar radiation) that reach the Earth. This energy can be converted into other forms of energy, such as heat and electricity.
In the 1830s, the British astronomer John Herschel famously used a solar thermal collector box (a device that absorbs sunlight to collect heat) to cook food during an expedition to Africa. Today, people use the sun's energy for lots of things.
Solar Energy Can Be Used for Heat and Electricity
When converted to thermal (or heat) energy, solar energy can be used to:
- Heat water — for use in homes, buildings, or swimming pools
- Heat spaces — inside homes, greenhouses, and other buildings
Solar energy can be converted to electricity in two ways:
- Photovoltaic (PV devices) or “solar cells” change sunlight directly into electricity. Individual PV cells are grouped into panels and arrays of panels that can be used in a wide range of applications ranging from single small cells that charge calculator and watch batteries, to systems that power single homes, to large power plants covering many acres.
- Concentrating Solar Power Plants generate electricity by using the heat from solar thermal collectors to heat a fluid which produces steam that is used to power the generator. Out of the 11 known concentrating solar power generating units operating in the United States at the end of 2008, 9 of these are in California, 1 in Arizona, and 1 in Nevada.
Two drawbacks of solar energy are:
- The amount of sunlight that arrives at the Earth's surface is not constant. It depends on location, time of day, time of year, and weather conditions.
- Because the sun doesn't deliver that much energy to any one place at any one time, a large surface area is required to collect the energy at a useful rate.
Energy from Moving Air
How Uneven Heating of Water and Land Causes Wind
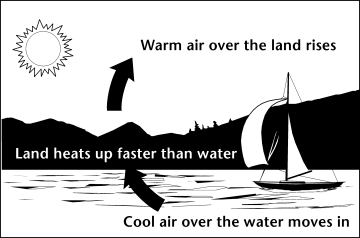
Source: National Energy Education Development Project (Public Domain)
Wind is simply air in motion. It is caused by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun. Because the Earth's surface is made of very different types of land and water, it absorbs the sun's heat at different rates. One example of this uneven heating can be found in the daily wind cycle.
The Daily Wind Cycle
During the day, the air above the land heats up more quickly than the air over water. The warm air over the land expands and rises, and the heavier, cooler air rushes in to take its place, creating wind. At night, the winds are reversed because the air cools more rapidly over land than over water.
In the same way, the atmospheric winds that circle the earth are created because the land near the Earth's equator is heated more by the sun than the land near the North and South Poles.
Wind Energy for Electricity Generation
Today, wind energy is mainly used to generate electricity. Wind is a renewable energy source because the wind will blow as long as the sun shines.
Energy From Moving Water
 Hydropower Generates Electricity Hydropower Generates Electricity
Hydropower is the renewable energy source that produces the most electricity in the United States. It accounted for 6% of total U.S. electricity generation and 67% of generation from renewables in 2008.
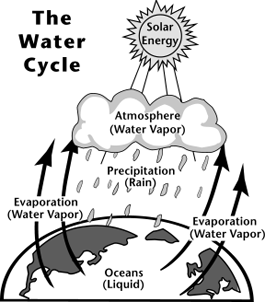
Hydropower Relies on the Water Cycle
Understanding the water cycle is important to understanding hydropower. In the water cycle:
- Solar energy heats water on the surface, causing it to evaporate.
- This water vapor condenses into clouds and falls back onto the surface as precipitation (rain, snow, etc.).
- The water flows through rivers back into the oceans, where it can evaporate and begin the cycle over again.
Mechanical Energy Is Harnessed from Moving Water
The amount of available energy in moving water is determined by its flow or fall. Swiftly flowing water in a big river, like the Columbia River that forms the border between Oregon and Washington, carries a great deal of energy in its flow. Water descending rapidly from a very high point, like Niagara Falls in New York, also has lots of energy in its flow.
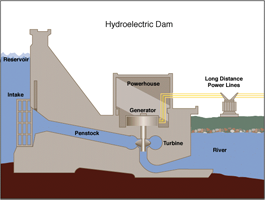 In either instance, the water flows through a pipe, or penstock, then pushes against and turns blades in a turbine to spin a generator to produce electricity. In a run-of-the-river system, the force of the current applies the needed pressure, while in a storage system, water is accumulated in reservoirs created by dams, then released as needed to generate electricity. In either instance, the water flows through a pipe, or penstock, then pushes against and turns blades in a turbine to spin a generator to produce electricity. In a run-of-the-river system, the force of the current applies the needed pressure, while in a storage system, water is accumulated in reservoirs created by dams, then released as needed to generate electricity.
History of Hydropower
Hydropower is one of the oldest sources of energy. It was used thousands of years ago to turn a paddle wheel for purposes such as grinding grain. Our Nation's first industrial use of hydropower to generate electricity occurred in 1880, when 16 brush-arc lamps were powered using a water turbine at the Wolverine Chair Factory in Grand Rapids, Michigan.
The first U.S. hydroelectric power plant opened on the Fox River near Appleton, Wisconsin, on September 30, 1882.
Because the source of hydroelectric power is water, hydroelectric power plants must be located on a water source. Therefore, it wasn't until the technology to transmit electricity over long distances was developed that hydropower became widely used.
|
|
 National and international wind energy industries and wind power technologies shall meet under a specialized exhibition, WindTech Istanbul, between the dates of 13-16 October 2010 in Istanbul for the first time in Turkey. WindTech is an exhibition, which targets the wind energy sector and which meets this sector under single roof.
National and international wind energy industries and wind power technologies shall meet under a specialized exhibition, WindTech Istanbul, between the dates of 13-16 October 2010 in Istanbul for the first time in Turkey. WindTech is an exhibition, which targets the wind energy sector and which meets this sector under single roof.


 Green (Renewable) Energy
Green (Renewable) Energy

 Biodiesel is renewable, nontoxic, and biodegradable. Compared to diesel, biodiesel burns significantly cleaner. It produces fewer air pollutants like particulates, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and air toxics. However, it does slightly increase emissions of nitrogen oxides.
Biodiesel is renewable, nontoxic, and biodegradable. Compared to diesel, biodiesel burns significantly cleaner. It produces fewer air pollutants like particulates, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and air toxics. However, it does slightly increase emissions of nitrogen oxides. What Is Ethanol?
What Is Ethanol? Ethanol Is Blended With Gasoline
Ethanol Is Blended With Gasoline
 Burning biomass is not the only way to release its energy. Biomass can be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as methane gas or transportation fuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel.
Burning biomass is not the only way to release its energy. Biomass can be converted to other useable forms of energy, such as methane gas or transportation fuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel. The sun has produced energy for billions of years. Solar energy is the sun’s rays (solar radiation) that reach the Earth. This energy can be converted into other forms of energy, such as heat and electricity.
The sun has produced energy for billions of years. Solar energy is the sun’s rays (solar radiation) that reach the Earth. This energy can be converted into other forms of energy, such as heat and electricity.
 Hydropower Generates Electricity
Hydropower Generates Electricity In either instance, the water flows through a pipe, or penstock, then pushes against and turns blades in a turbine to spin a generator to produce electricity. In a run-of-the-river system, the force of the current applies the needed pressure, while in a storage system, water is accumulated in reservoirs created by dams, then released as needed to generate electricity.
In either instance, the water flows through a pipe, or penstock, then pushes against and turns blades in a turbine to spin a generator to produce electricity. In a run-of-the-river system, the force of the current applies the needed pressure, while in a storage system, water is accumulated in reservoirs created by dams, then released as needed to generate electricity.

